Protection needed for emerging mining hotspots

Growing demand for metals necessary for the transition to a low carbon future will lead to more mining in high-risk areas, according to University of Queensland research.
Dr Éléonore Lèbre and researchers from UQ’s Sustainable Minerals Institute identified mining ‘hotspots’ by looking at areas where competition over mining resources such as water and land is likely to negatively impact surrounding communities.
“Past research has raised concerns about the environmental, social and governance pressures that come from increased mining but they have never assessed the risks on a global scale using quantitative data,” Dr Lèbre said.
“By applying seven categories of risk – three environmental, three social and one governance indicator – we were able to map where these mining hotspots would exist and the metals involved.
“All the metals we analysed are necessary for the transition to a low-carbon future.
“Some exhibit particularly risky profiles, with 84 per cent of platinum and 70 per cent of cobalt resources located in high-risk contexts.
“Major metals like iron and copper are rarely talked about in the energy transition discussion, but they will be needed in large quantities, and are set to disturb big chunks of land as production volumes increase.
“Australia, the United States and China will be the most affected, having the largest clusters of mines located in potential high-risk contexts.
“Good governance in these countries will be key to ensure the energy transition happens without unleashing unacceptable social and environmental impacts induced by mining.”
The study looked at over 6800 mining projects of 20 different metals around the world.
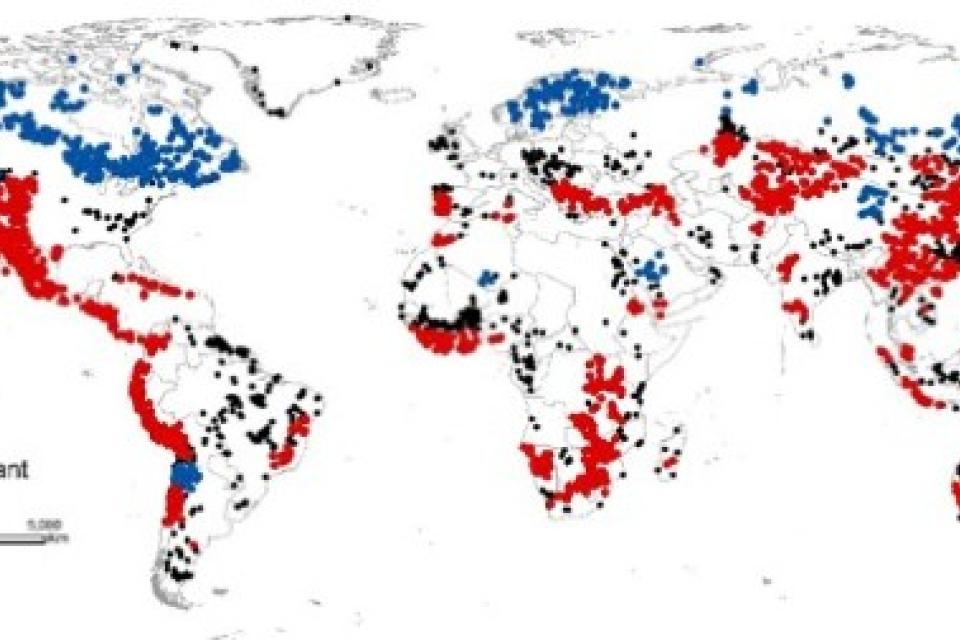
Mining hotspots identified by the researchers on world map.
Leader of SMI’s Complex Orebodies Program Professor Rick Valenta said the industry would need to demonstrate it can effectively address these risks in order to overcome future obstacles to supply.
“The rise of renewable energy technologies and electric vehicles will mean that metals, such as lithium, cobalt, copper and nickel will become increasingly important for society,” Professor Valenta said.
“In order to access the increasingly high-risk orebodies necessary to meet this demand, the mining industry needs to prove its environmental and social responsibility to an increasingly conscious public.”
This study is published in Nature Communications. (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18661-9).
Media: Dr Eléonore Lèbre, Research Fellow, e.lebre@uq.edu.au, +61 7 3346 4137; Connor Pound, Media Officer, c.pound@uq.edu.au, +61 447 812 081
Related articles

New data reveals how Australia’s threatened reptiles and frogs are disappearing – and what we have to do

Long-sought environmental law reform is finally here. But will the compromise deal actually protect nature?
Media contact
UQ Communications
communications@uq.edu.au
+61 429 056 139
