Recurrent pregnancy loss linked to increased stroke risk later in life
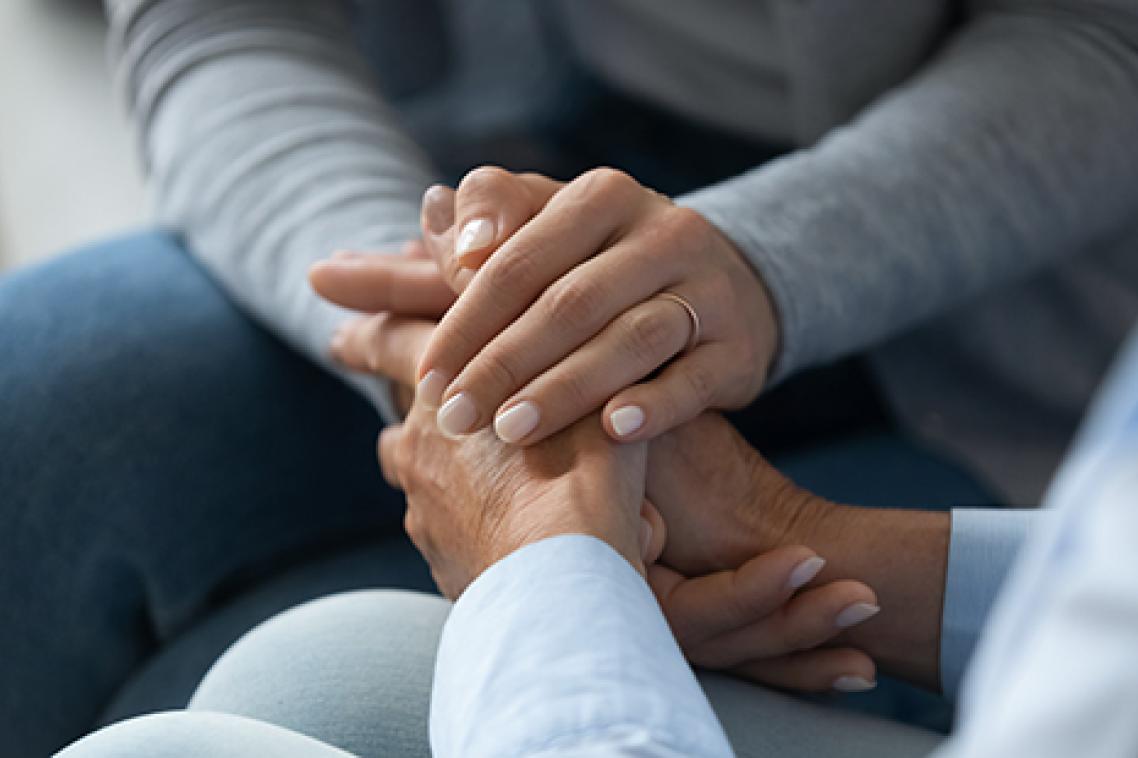

Women with a history of miscarriage and stillbirth have a higher risk of stroke in later life, according to University of Queensland research.
The study compared pooled data from more than 610,000 women in Australia, China, Japan, Netherlands, Sweden, UK and USA, and found the risk increased with multiple pregnancy loses.
Senior author, UQ’s Professor Gita Mishra from the UQ School of Public Health, said many women were unaware that their experiences during pregnancy acted as an early alert for the risk of diseases in later life.
“This is the first study big enough to demonstrate a robust link between stroke and recurrent miscarriage and very rare events like recurrent stillbirths,” Professor Mishra said.
“It’s vital for older women who have suffered multiple miscarriages or stillbirth to share their history with their GPs, no matter how much time has passed.”
The study, led by PhD candidate Ms Chen Liang, showed that women’s risk of having a stroke in later life climbed with each miscarriage.
Women who had miscarried once had a 7 per cent higher risk of fatal and non-fatal strokes than women who hadn’t experienced miscarriage during their pregnancy.
The risk was 12 per cent higher for a non-fatal stroke and 26 per cent higher for a fatal stroke, for two miscarriages.
After three or more miscarriages, the risk increased to 35 per cent for a non-fatal stroke and 82 per cent for a fatal stroke compared with other women.
While one in 5 pregnancies (19 per cent) end in miscarriage, less than 5 per cent of women will experience multiple miscarriages, and about 1 per cent will experience three or more miscarriages.
“In real terms what we see is– among women who had three or more miscarriages 41 out of every 1000 experienced a non-fatal stroke and 12 in 1000 had a fatal stroke, compared to 29 non-fatal strokes and 7 fatal strokes for every 1000 women who had never miscarried,” Professor Mishra said.
Similarly, the risk of stroke increased for each stillbirth a woman experienced compared to women with no history of stillbirth; after two stillbirths the risk of a non-fatal stroke was 29 per cent higher and the risk of a fatal stroke 26 per cent higher.
“For women who are still grieving and processing – this isn’t the time to worry about these findings,” Professor Mishra said.
“But, if you are heading into perimenopause, or if you’re post-menopausal, and have a history of multiple miscarriages or stillbirths, please talk to your GP about managing your health risks.
“Your doctor might recommend medication, but there are a lot of lifestyle changes you can make to reduce your risk of stroke.”
The Stroke Foundation recommends maintaining a healthy weight, exercising for 30 minutes a day, stopping smoking, and managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
This research was made possible through InterLACE, an international collaboration which pooled data from 618,851 women who took part in eight separate studies in Australia, China, Japan, Netherlands, Sweden, the UK, and the USA.
The research is published in BMJ (DOI: 10.1136/bmj-2022-070603).
Media: Professor Gita Mishra, g.mishra@uq.edu.au; UQ Communications, med.media@uq.edu.au, +61 (0)436 368 746.
Topics
Related articles

Nature versus nurture question addressed in landmark study
A better way to assess cardiovascular health
Media contact
UQ Communications
communications@uq.edu.au
+61 429 056 139
