Cell protein discovery points to healthier ageing
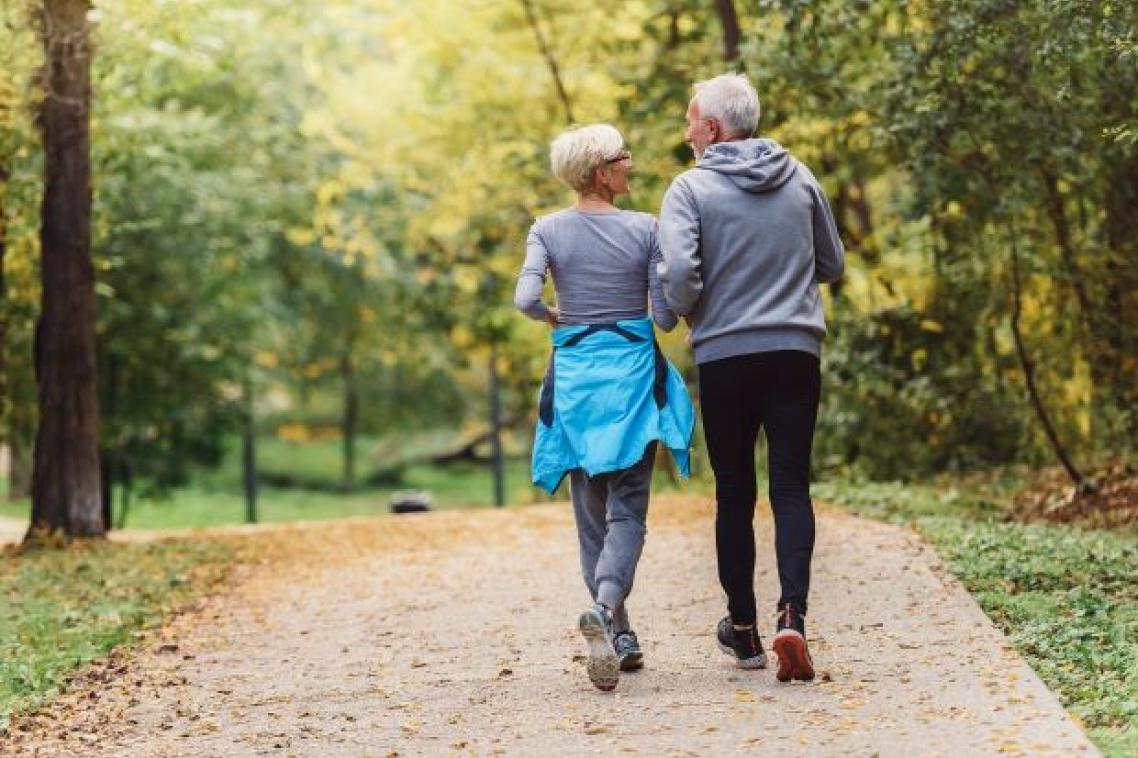

Researchers at The University of Queensland have found an anti-ageing function in a protein deep within human cells.
Associate Professor Steven Zuryn and Dr Michael Dai at the Queensland Brain Institute have discovered that a protein called ATSF-1 controls a fine balance between the creation of new mitochondria and the repair of damaged mitochondria.
Mitochondria, with their own DNA, produce energy within cells to power biological functions but the toxic by-products of this process contribute to the rate at which the cell ages.
“In conditions of stress, when mitochondrial DNA has been damaged, the ATSF-1 protein prioritises repair which promotes cellular health and longevity,” Dr Zuryn said.
As an analogy, Dr Zuryn likened the relationship to a race car needing a pitstop.
“ATSF-1 makes the call that a pitstop is needed for the cell when mitochondria need repairs,” he said.
“We studied ATFS-1 in C. elegans, or round worms and saw that enhancing its function promoted cellular health, meaning the worms became more agile for longer.
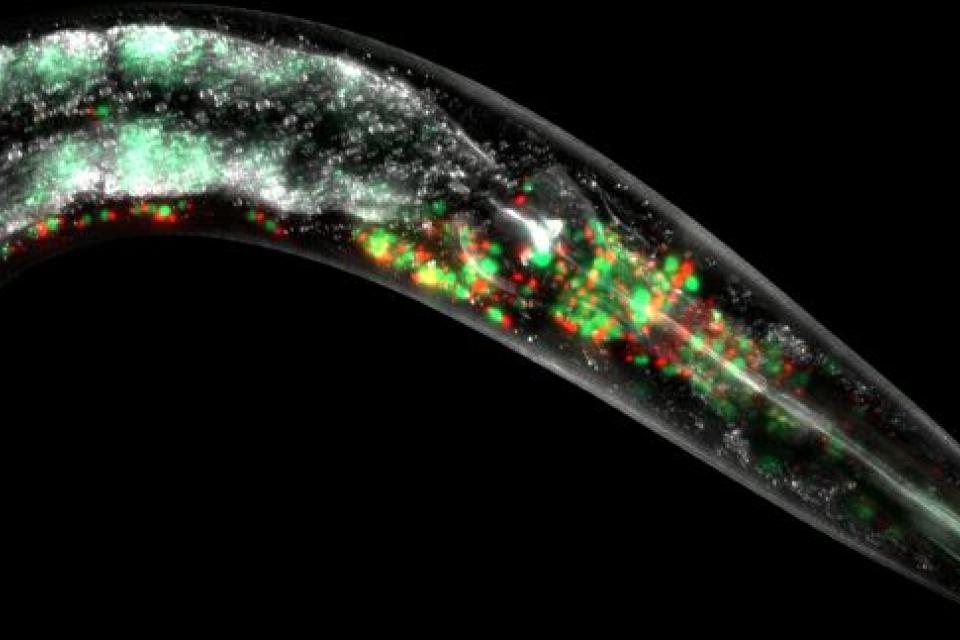
“Mitochondrial dysfunction lies at the core of many human diseases, including common age-related diseases such as dementias and Parkinson’s.
“Our finding could have exciting implications for healthy ageing and for people with inherited mitochondrial diseases.”
Understanding how cells promote repair is an important step towards identifying possible interventions to prevent mitochondrial damage.
“Our goal is to prolong the tissue and organ functions that typically decline during ageing by understanding how deteriorating mitochondria contribute to this process,” Dr Dai said.
“We may ultimately design interventions that keep mitochondrial DNA healthier for longer, improving our quality of life."
This research was published in Nature Cell Biology.
Image above left: UQ researchers studied proteins in the mitochondria of cells in round worms, lit up red and green, and found one which prioritises repair promoting cellular health and longevity.
Media: QBI Communications, communications@qbi.uq.edu.au, Merrett Pye +61 422 096 049; Elaine Pye +61 415 222 606.
Topics
Related articles

Nature versus nurture question addressed in landmark study
A better way to assess cardiovascular health
Media contact
UQ Communications
communications@uq.edu.au
+61 429 056 139
