Biomedicine shows the way to future food crops
University of Queensland researchers have for the first time introduced genetic material into plants via their roots, opening a potential pathway for rapid crop improvement.
Professor Bernard Carroll from UQ’s School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences said nanoparticle technology could help fine-tune plant genes to increase crop yield and improve food quality.
“Traditional plant breeding and genetic modification take many generations to produce a new crop variety, which is time-consuming and expensive,” Professor Carroll said.
“We have succeeded in having plant roots absorb a benign nanoparticle which was developed by Professor Gordon Xu’s group at UQ for the delivery of vaccines and cancer treatments in animals.
“Plant cell walls are rigid and wood-like, much tougher than human or animal cells so we coated the nanoparticle with a protein that gently loosens the plant cell wall.
“The protein coating helped the nanoparticle break through the cell walls to deliver a synthetic mRNA cargo into plants for the first time.”
mRNAs are natural messenger molecules containing genetic instructions to build and enhance all forms of life.
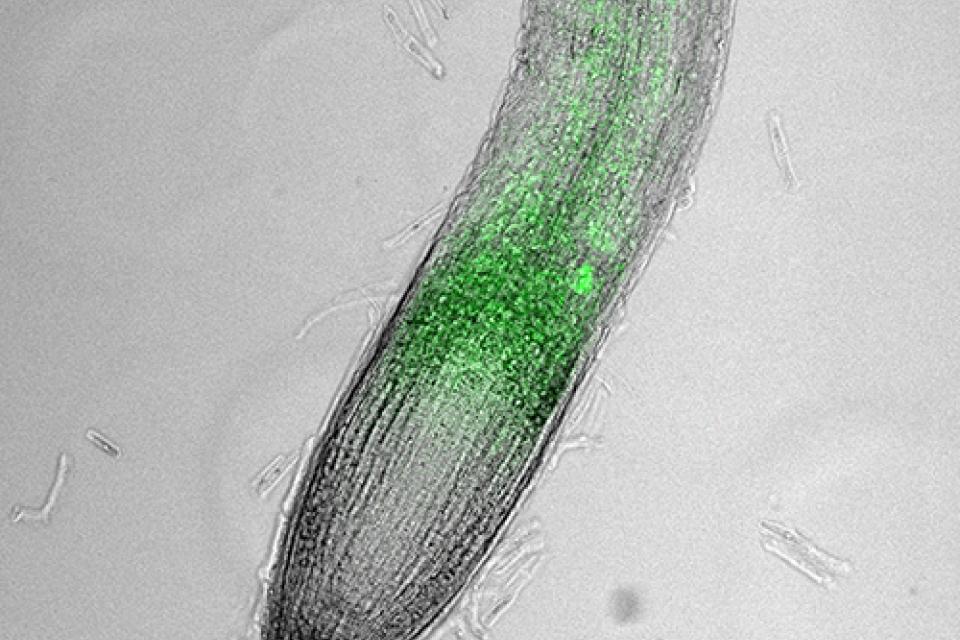
“It was surprising that rather than delivering all of its load in the first cell it entered, the nanoparticle travelled with water through the plant distributing the mRNA as it went,” Professor Carroll said.
“This is exciting because with further improvement, the technology could potentially be used in the future to produce new crop varieties more quickly.
“With further research we could target an issue with a crop such as flavour or quality and have a new variety without the need for a decade of cross breeding or genetic modification.
“Similar to how an mRNA vaccine produces a protein to stimulate the immune system and then degrades away, the mRNA we deliver into plants is expressed transiently and then disappears.”
The nanoparticle technique has been patented by UQ’s commercialisation company UniQuest, which is now seeking partners to further develop the technology.
The research team included Professor Zhi Pin (Gordon) Xu and Dr Jiaxi Yong at UQ’s Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology and Queensland Alliance for Agriculture and Food Innovation.
The research has been published in Nature Plants.
Image above left: Microscope view of a root tip and the progression of synthetic mRNA that produces a green fluorescent protein.
Media contact
UQ Communications
communications@uq.edu.au
+61 429 056 139
Related articles

Staying physically active cuts risk of early death by 40 per cent

Medicinal cannabis is big business. But the latest clampdown won’t curb unsafe prescribing
Media contact
UQ Communications
communications@uq.edu.au
+61 429 056 139
