Newborn vitamin D deficiency linked to higher risk of ADHD, schizophrenia, autism
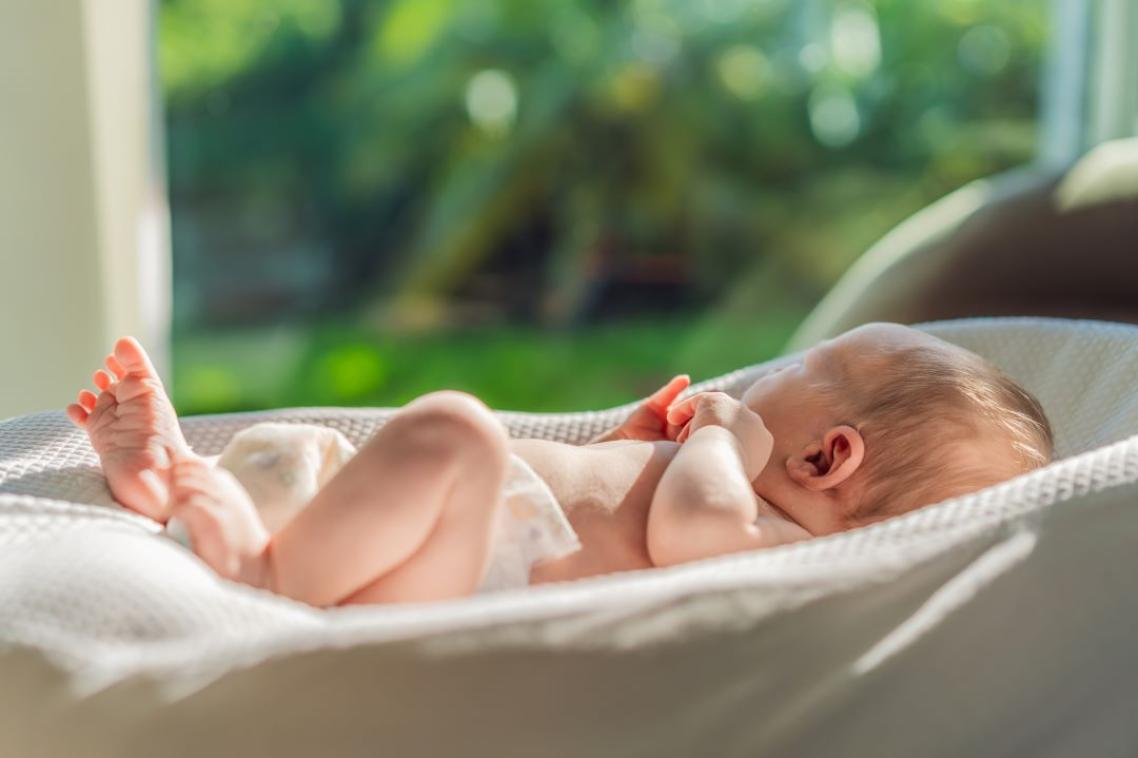

(Photo credit: Adobe stock )
In the largest population study of its kind, researchers examined vitamin D status of 71,793 people, many of whom had a mental health disorder diagnosed during childhood and early adulthood.
Professor John McGrath from UQ’s Queensland Brain Institute, led the study that was based at the National Centre for Register-Based Research, Aarhus University, and the State Serum Institute in Denmark.
He said they examined 6 mental disorders: major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and anorexia nervosa.
“We found evidence that people with lower vitamin D concentration as a baby had an increased risk of schizophrenia, ASD and ADHD,” Professor McGrath said.
“Previous research had linked neonatal vitamin D deficiency with an increased risk of schizophrenia and autism, but this study examined a wider range of mental disorders, and included evidence based on two vitamin D-related biomarkers and related genetics.”
Professor McGrath said their research suggested that vitamin D supplements during pregnancy and early life could help reduce the risk of mental disorders in adulthood.
“Vitamin D is important for a baby’s brain development, and low vitamin D levels are common in pregnant women across the globe,’’ he said.
“This is why many countries recommended the use of vitamin D supplements during pregnancy.
“Similar to how folate supplements are recommended during pregnancy to prevent spina bifida, our research suggest that optimising vitamin D levels in early life may reduce the risk of several neurodevelopmental disorders.”
The researchers analysed data from the iPSYCH study, which was founded in 2012 to investigate mental disorders in Denmark.
Vitamin D usually comes from sun exposure but can also be found in some foods and supplements.
The research is published in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Professor McGrath’s work is funded by the Danish National Research Foundation, the Queensland Centre for Mental Health Research and The University of Queensland.
The iPSYCH project is funded by the Lundbeck Foundation.
Topics
Related articles

Nature versus nurture question addressed in landmark study
A better way to assess cardiovascular health
Media contact
UQ Communications
communications@uq.edu.au
+61 429 056 139
